Page History: Chart Element
Compare Page Revisions
Page Revision: 2014/07/26 19:07

|
Chart Element
|
| Info |
| Category: |
Psychophysical Methods |
|
AddIn: |
Psychophysical Methods |
| Creator: |
OkazoLab Team |
|
Scope: |
Global |
| Owns Snippets: |
no |
|
Usage: |
Status Screen,Snippets |
The chart element plots any arbitrary data using different chart types and estimates the common descriptive statistics, e.g. mean, median, SD and SE.
Description
The chart element is capable of plotting arbitrary data using different chart types and data groups. The element auto-updates its chart, when data is modified or added. The generated chart can be shown either on the presentation or
status screen. The element can be broadly used, when you want to monitor experimental effects or their development over a course of an experiment. In addition, the chart element returns the descriptive statistics of the collected data, e.g. mean, median, SD and SE values.
Snapshots
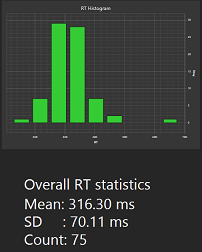 Bar chart showing
distribution of RTs | 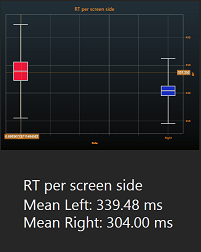 Box-and-Whisker Plot showing
difference between 2 conditions |
Data representation
Before you start using the Chart element, it's important to understand how it handles data. The Chart operates with one or more datasets, and you have to define in advance how many datasets will be used and plotted together on the chart. Each dataset contains a number of data points, which can be defined in different formats:
- A numerical pair of X-Y values (a dataset may contain any number of the X-Y pairs that may overlap)
- Indexed Y values (For each Y value in a dataset, its X counterpart is defined by an value's index in the dataset. Correspondingly, there is only one Y value for every integer index from 0 to N)
- Text values, or pairs of X-Text values (the text data points are normally used to produce labels for chart's axis).
Check the following screenshot of the chart designer, in which 3 datasets with different data points are previewed:
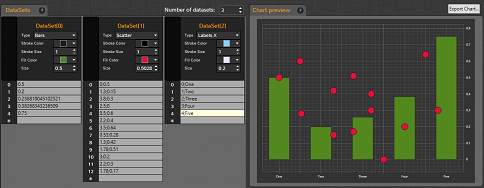 Datasest with different data points (left) and the generated chart (right).
The datasets include: 1) indexed Y values (bars), b) X-Y pairs (scatter),
c) X-Text values (labels for the X axis)
Click on the screen shot to enlarge |
You should use the same data point type in each dataset.
Chart designer
The chart element has a visual designer that allows to manage datasets and visualization settings. Once you decide what data you want to visualize in an experiment, you can open the designer via the Chart designer property of the element.
Plot Types
Basic Plots
| / | Lines | Bars | Scatter | Maintain | Histogram |
|---|
| Description |
|---|
| Datapoints |
|---|
| Example |
|---|
|
Statistics Plots
Practical Use
Technique 1
- Step 1
- Step 2
Technique 2
- Step 1
- Step 2
// Check the trial outcome. Result and RT just other user variables
// insert code snippet here..
Element actions aligned with different epochs of the parent event
| Epoche | Actions |
|---|
| Initialized | The camera starts capturing video |
| Rendered |
| Activating |
| Activated |
| Running | The camera output is captured and rendered via the Video Output property, if the latter is bound to the status screen |
| Deactivated |
| Deinitialized | The camera stops capturing video |
Notes
Insert Notes here..
Properties
Generic Properties
| Name | Description | Constraints | Value Type | Upon Runtime Change |
|---|
| Settings |
| name | description | attributes | type String | |
+=== Properties inherited from clElement ===
Inherited properties of clElement
| Name | Description | Constraints | Value Type | Upon Change |
|---|
| Control |
| Is Enabled | If set to false the element is completely omitted when the experiment is run. | | Boolean |
|
| Title | Title of the element. | | String |
|